
In our next unbalanced half reaction, liquid chloride anions Therefore, liquid sodium ions are reduced to form liquid sodium metal
#Cathode reaction in electrolytsis of cucl2 plus
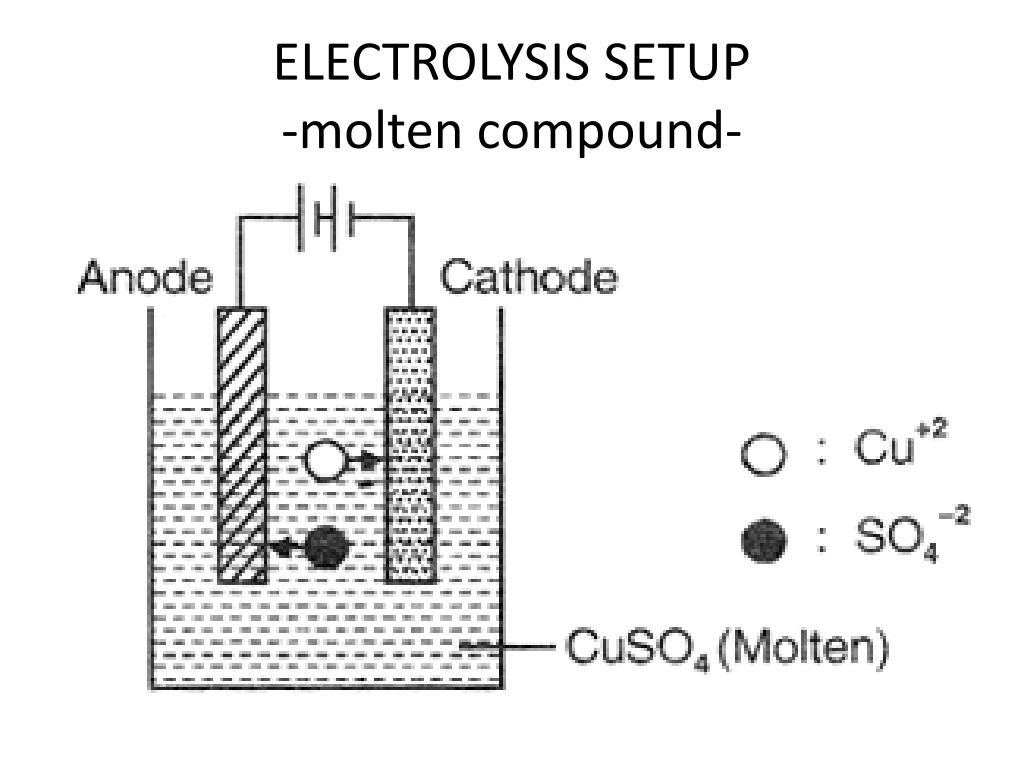
So going from plus one to zero is a decrease or a reduction Liquid sodium ions haveĪn oxidation number of plus one and liquid sodium metal has an oxidation number of zero. That this is a reduction half reaction is toĪssign oxidation numbers. Ion is gaining an electron, this represents the In one half reaction, liquid sodium ions react with an electron toįorm liquid sodium metal. Of electrolytic cell, let's look at the half reactions that will occur in the cell. Electrolytic cells use an electric current to drive a thermodynamically unfavorable reaction. If water is oxidized, then oxygen gas is produced instead of the neutral form the anion, and if water is reduced then hydrogen gas forms instead of the neutral form of the cation. For reduction whichever is more easily reduced, the cations or water, will be reduced first. For the oxidation whichever is more easily oxidized, the anion or water, will be oxidized first. The same logic applies here as it does in molten salt mixture cells though. The same idea applies to anions, the anion which is more easily oxidized, the one with the more negative reduction potential, is oxidized first.Įlectrolytic cells in aqueous solutions become problematic because of the possibility of oxidizing or reducing water instead of the target ions. Which in this case is the sodium cation which turns into solid sodium, and the liquid potassium remains unreacted. The cation which is more easily reduced, the one with the more positive reduction potential, is reduced.

For example, if we have a molten salt mixture of sodium chloride and potassium chloride, the chloride will still be oxidized since it’s the only anion, but either the sodium or potassium cations have the possibility of reducing.

If the solution is a molten salt with multiple salts present, then there are different possibilities as to which cation gets reduced and which anion gets oxidized. And the anions get oxidized into their neutral chemicals like 2Cl^(-)(l) → Cl2(g) + 2e. The cations get reduced into neutral chemicals like Na^(+)(l) + e- → Na (s). If the solution is a molten salt with only a single salt present, like in the sodium chloride example, then the reaction is straightforward. The solutions are usually either molten salt or aqueous. Yes, we have to take the solution itself into account too in electrolytic cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
